Node Overview
Running a node on the TEN network involves participating in the network’s transaction processing, batching, and roll-up mechanisms. As a node operator, you will play a critical role in maintaining the network’s security, scalability, and efficiency. Understanding the flow of transactions and the mechanics of batches and roll-ups is essential for effectively running a node and contributing to the network’s operation.
Transaction Flow (TX)
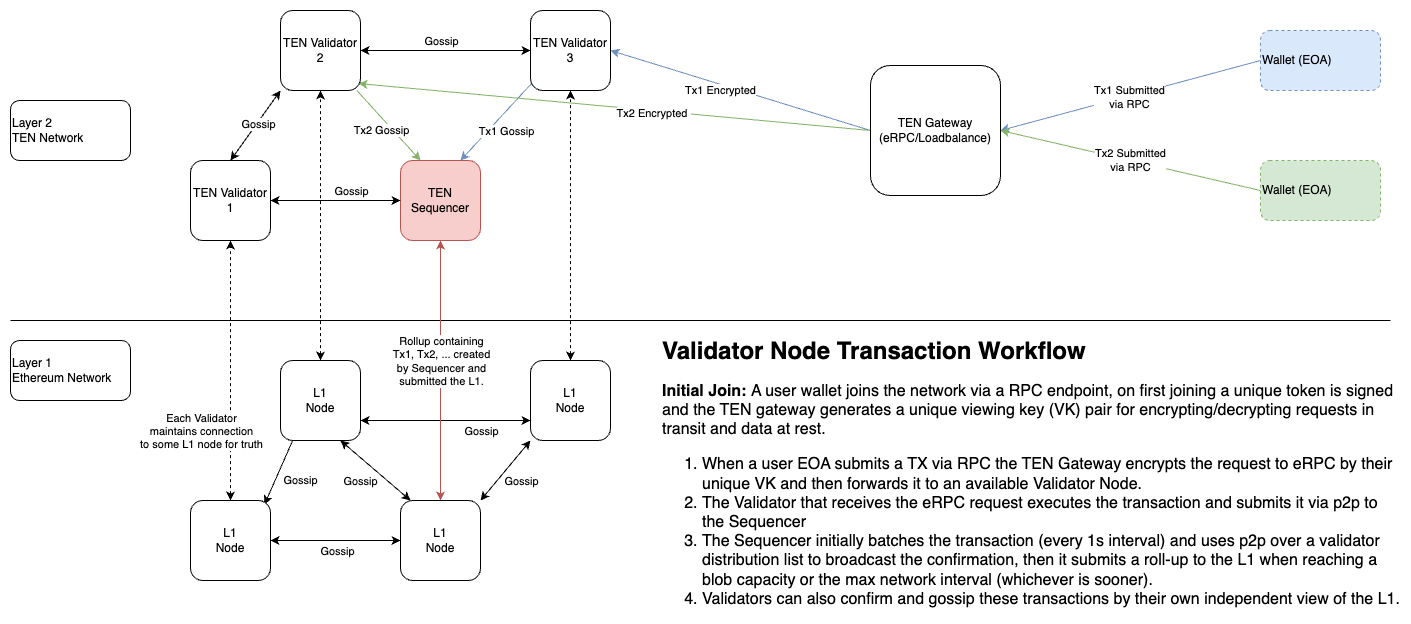
1. Transactions
Transactions are the fundamental operations executed on the TEN network, representing actions such as transferring value, interacting with smart contracts, or executing other network functions. Each transaction serves as a discrete unit of activity, altering the state of the network based on its payload.
2. Batches
Batches consist of multiple transactions grouped together on the TEN network, functioning similarly to blocks on the Ethereum network. By aggregating transactions into batches, the network enhances throughput and lowers latency, optimizing resource usage and improving overall efficiency.
3. Roll-ups
Roll-ups are a layer 2 scaling mechanism employed by the TEN network to securely aggregate and process transactions off-chain, before submitting a compressed version of these transactions to the Ethereum mainnet (Layer 1) for finalization. This approach significantly boosts throughput and reduces latency while maintaining the security guarantees of the Ethereum network.
Gateway
The TEN Gateway is a network managed service and load balancer that routes transactions to the appropriate TEN validator nodes. It is responsible for securely encrypting and decrypting transactions, ensuring that sensitive data remains confidential throughout the transaction process. Validators interact with the Gateway to receive transactions, process them, and submit them to the Sequencer for batching and roll-up.
Node Types
There are two types of nodes in the TEN network: Sequencers and Validators. They use the same software but have different roles and responsibilities. As a node operator you will be running a Validator node, but it is important to understand the role of Sequencers in the network.
Sequencer
The TEN Sequencer is a central node that is responsible for ordering transactions, generating new batches, and creating roll-ups on the TEN network. It is the only node that can create new batches and is responsible for broadcasting these to the network, as well as submitting them to the Ethereum mainnet via roll-up.
Validator
A TEN Validator is decentralized node that participates in the TEN network by processing transactions, validating transactions and batches against Ethereum L1 roll-ups, and providing data availability. The participation of multiple validators ensures the network’s security and integrity.